International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 19/fev/2025;38:e20240067.
Virtual Reality and Physical Activity in Patients with Heart Failure: Technology Validation and User Satisfaction – Pilot Study
Abstract
Background
Digital health uses innovative information technology for healthcare needs. Virtual reality (VR) is increasingly adopted in healthcare, including cardiovascular rehabilitation (CVR), to improve performance and adherence. However, digital interventions must consider users’ perspectives to prevent VR from becoming a barrier.
Objective
This study aimed to assess the usability and enjoyment of physical activity associated with VR among inpatients with heart failure (HF).
Method
A prospective pilot study was conducted with ten patients diagnosed with HF. Participants completed an exercise program on a cycle ergometer with immersive VR for lower limb training. Anxiety and depression symptoms, physical activity enjoyment, and system usability were evaluated. Statistical analysis included descriptive and inferential analyses with a 5% significance level (p<0.05). Pearson’s test was used for correlation analysis.
Results
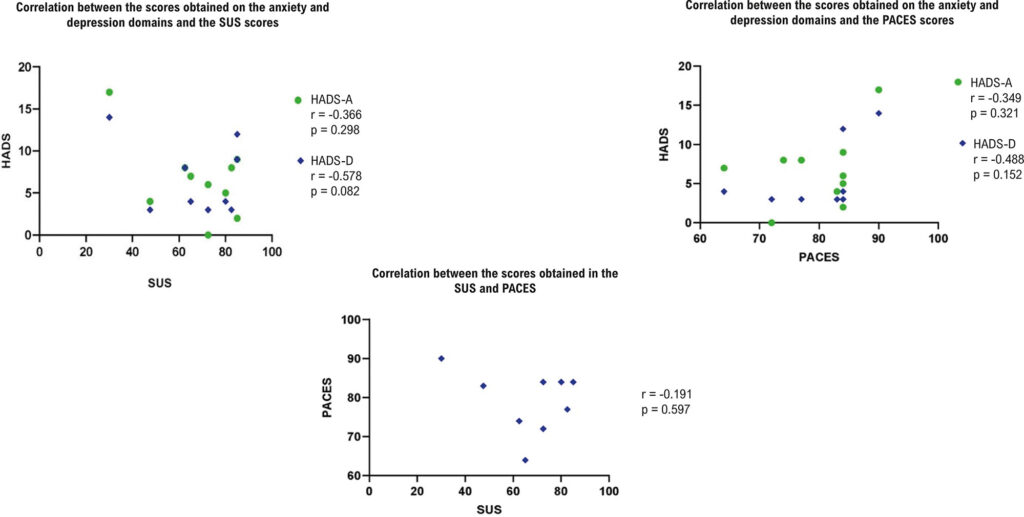
The population’s tendency to experience anxiety and depression was evaluated, and the sample favorably assessed the system’s usability, with a mean score of 68.2 (standard deviation ±17.8); exercise enjoyment scored 79.6 (±7.7). No significant correlations were found between anxiety and depression profiles and usability or exercise enjoyment, suggesting further study phases.
Conclusions
VR can complement rehabilitation programs for HF patients, potentially improving performance and adherence. Additional research is required to evaluate the effectiveness of VR-associated physical activity on clinical outcomes in HF patients.
Palavras-chave: Virtual reality; digital health; heart failure; rehabilitation
580