International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 29/maio/2025;38:e20240187.
Six-Month Remote Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Heart Failure Using Messaging Applications on Smartphones
Abstract
Background:
Patients with chronic heart failure (HF) require outpatient monitoring after hospital discharge. The ability to use a smartphone with a personal messaging application may help.
Objectives:
Tis study aimed to investigate the feasibility of remote monitoring and evaluate its impact on treatment adherence and prognosis in patients with HF.
Methods:
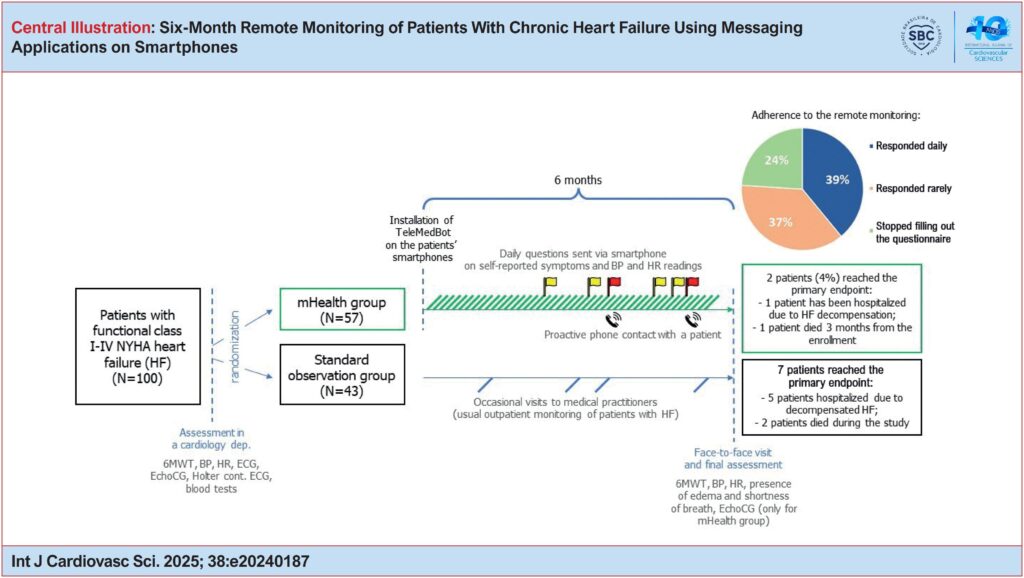
A total of 100 patients were enrolled in the study: 57 patients in the mHealth group and 43 in the control group. The observation period lasted six months. Remote monitoring included a daily survey sent to patients via a personal messaging application. This was an open, randomized trial. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results:
After six months, 46 patients (mean age 61.52 ± 13.05 years, 34 men) in the mHealth group and 43 patients (mean age 60.07 ± 10.19 years, 27 men) in the control group completed the study. A total of 11 patients were lost to follow-up. In the mHealth group, two patients (4%) reached the primary endpoint, compared to seven patients (7%) in the control group.
Conclusion:
The effectiveness of remote monitoring for patients with HF using self-reporting via a smartphone messaging application was demonstrated. Patient adherence to self-reporting was found to be 76%. Those in the mHealth group who reported regularly and consistently demonstrated greater engagement in self-monitoring of vital signs and higher adherence to prescribed therapy.
Palavras-chave: Heart Failure; Remote Patient Monitoring; Telemedicine
267