International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 15/jan/2021;35(1):140-4.
Pulmonary Embolism in Patients with Covid-19 in Direct Oral Anticoagulant
Introduction
The global pandemic caused by the new coronavirus (COVID-19) has been promoting major challenges and unprecedented clinical decisions in the medical scenario. Currently, according to the World Health Organization, the disease affects over 185 countries, with over 12 million people infected and nearly 500 thousand deaths.
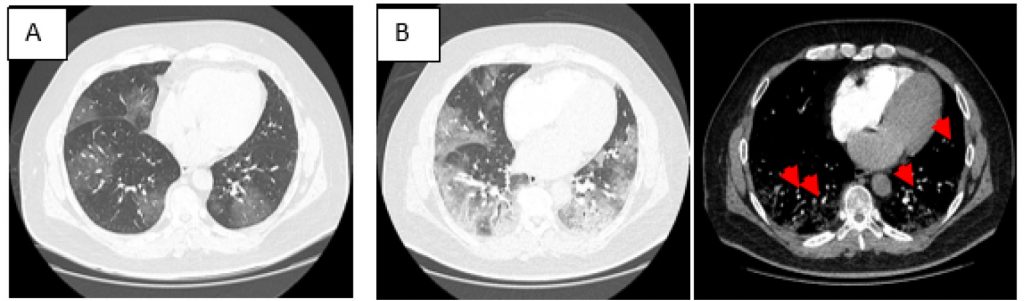
Among the most serious manifestations of the syndrome, the high prevalence of thromboembolic events, up to 31% of the patients hospitalized in intensive care units, according to an international series, calls attention.– Different mechanisms of action related to the infection by SARS-CoV-2 may be related to thrombosis: excessive inflammation, tissue hypoxia, immobilization, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC); however, one question remains: Is the etiology linked to some specific effect of the virus or a reflex of the severity of the case? Despite the anticoagulant therapy emerging as a major weapon in the therapeutic arsenal, data is still scarce in the literature regarding the efficacy and safety of warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) in this specific setting. It should be highlighted that, of the 1.5 million people currently infected in Brazil, a significant number present a history of cardiovascular disease and are presently taking anticoagulants. This class of drugs may show serious interactions with investigational therapies currently employed for COVID-19, which could increase the risk of thrombotic or hemorrhagic events. In this context, it becomes imperative to highlight that the thrombosis associated with COVID-19 and anticoagulant therapy is a unique scenario and must be investigated.
[…]
Palavras-chave: COVID-19; Pandemics; Respiratory Acute Syndrome; Pulmonary Embolism; Anticoagulants
752