International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 23/ago/2018;31(6):562-8.
Option for the Radial versus Femoral Access in Coronary Intervention in Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Risk-Treatment Paradox
DOI: 10.5935/2359-4802.20180066
Abstract
Background:
In coronary procedures, although the radial approach protects patients from hemorrhagic complications, it is technically more complex than the femoral approach.
Objectives:
To test the hypothesis that the radial approach is the procedure of choice in ACS patients due to the high risk of bleeding; and to identify independent predictors of the choice for radial access.
Methods:
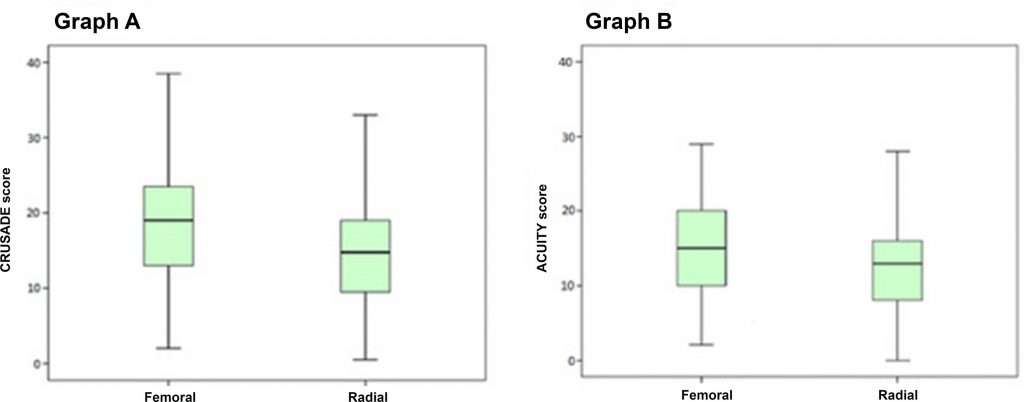
Patients admitted for ACS who underwent invasive coronary procedure were included. We registered the type of access (femoral or radial) chosen by the physician for the first angiography; the investigators did not interfere with this choosing process. Student’s t-test was used for comparisons between the CRUSADE and ACUITY scores. Predictors of radial access were compared between the groups. Statistical significance was defined by p < 0,05.
Conclusion:
The propensity to choose radial over femoral access in coronary intervention was not primarily influenced by patients’ bleeding risk. Predictors of this decision, identified in the study, indicated less complex patients, suggesting that the difficulty in performing the technique was a stronger determinant than its potential antihemorrhagic effect. (Int J Cardiovasc Sci. 2018; [online].ahead print, PP.0-0)
Palavras-chave: Angioplasty; Catheterism; Coronary Artery Disease; Percutaneous Coronary Intervention; Radial Artery; Femoral Artery; Stents
663