International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 15/ago/2025;38:e20250064.
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy on Electrocardiography and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Case–Control Pilot Study
Abstract
Background:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a condition characterized by abnormalities in kidney structure or function lasting more than 3 months. CKD is known to increase the risk of cardiovascular events, which may be predicted by electrocardiography (ECG) abnormalities, such as left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). ECG is widely used in under-resourced health care settings due to its practicality and accessibility.
Objective:
This study aimed to analyze the relationship between LVH and CKD using ECG.
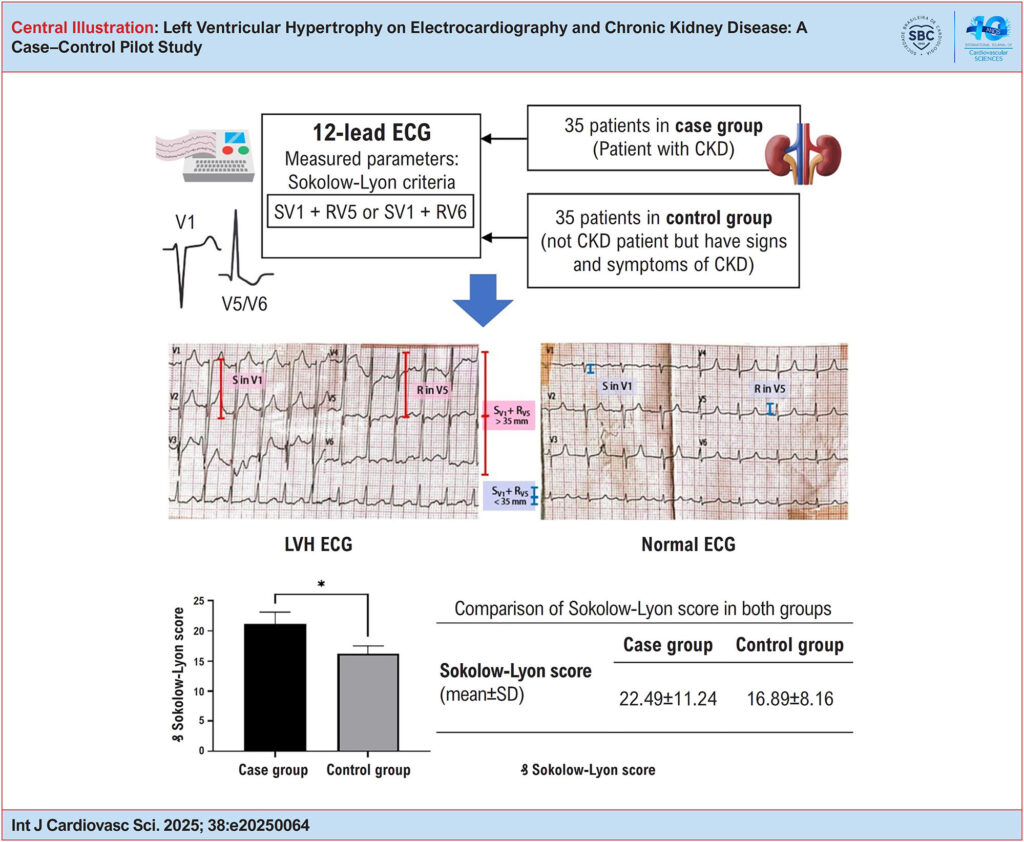
Methods:
This analytical observational study used a case–control design. The case group included patients diagnosed with CKD, while the control group consisted of patients presenting with signs and symptoms suggestive of CKD but without a confirmed diagnosis. Each group included 35 participants. Simple random sampling was used for the case group, and stratified random sampling for the control group. ECG examinations were performed, and measurements were taken using calipers in millimeters (mm). The Sokolow–Lyon criteria were applied to identify LVH. Data were analyzed using an independent t-test, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05.
Results:
The Sokolow–Lyon score was significantly higher in the case group than in the control group (p = 0.03).
Conclusion:
There is a significant association between LVH, as identified on ECG, and CKD. These findings may assist health professionals in resource-limited settings, where access to ECG is restricted.
317