International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 17/jun/2021;34(4):490-3.
Catheter Ablation in Neonate with Heart Failure Due to Incessant Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia
Abstract
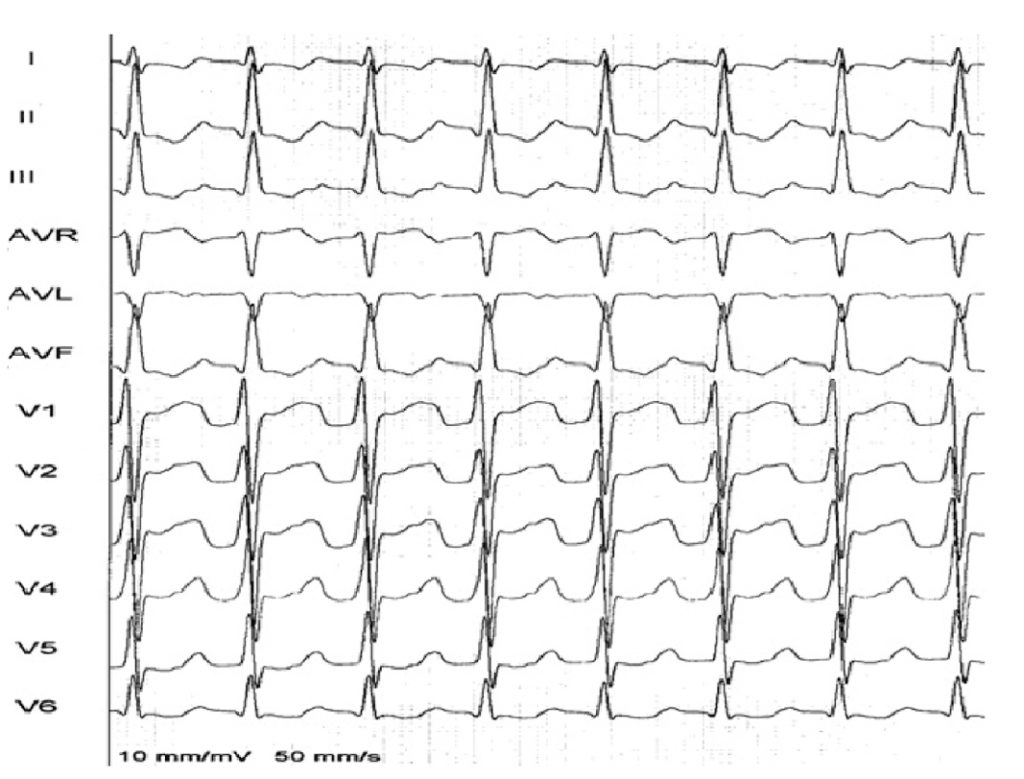
The atrioventricular (AV) reentrant tachycardia (AVRT) is the most common cause of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in the young pediatric population. Some newborns might present with congestive heart failure and require interventional treatment. Catheter ablation in small infants (<6 months and <5 kg) is still poorly performed and controversial due to high complications rate in this group of patients.1 We report a case of a 28 days old infant (3,5 kg) with a drug-refractory left accessory pathway mediated tachycardia and severe hemodynamic compromise, who underwent catheter ablation. Radiofrequency ablation should be part of the therapeutic arsenal in a context of drug-resistant supraventricular tachycardia with hemodynamic compromise, despite the greater risks of complications in this special population.
Palavras-chave: Newborn; Supraventricular Tachycardia; Heart Failure; Catheter ablation
397