International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 01/nov/2022;35(6):727-9.
Can Exercise Training Prevent Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy?
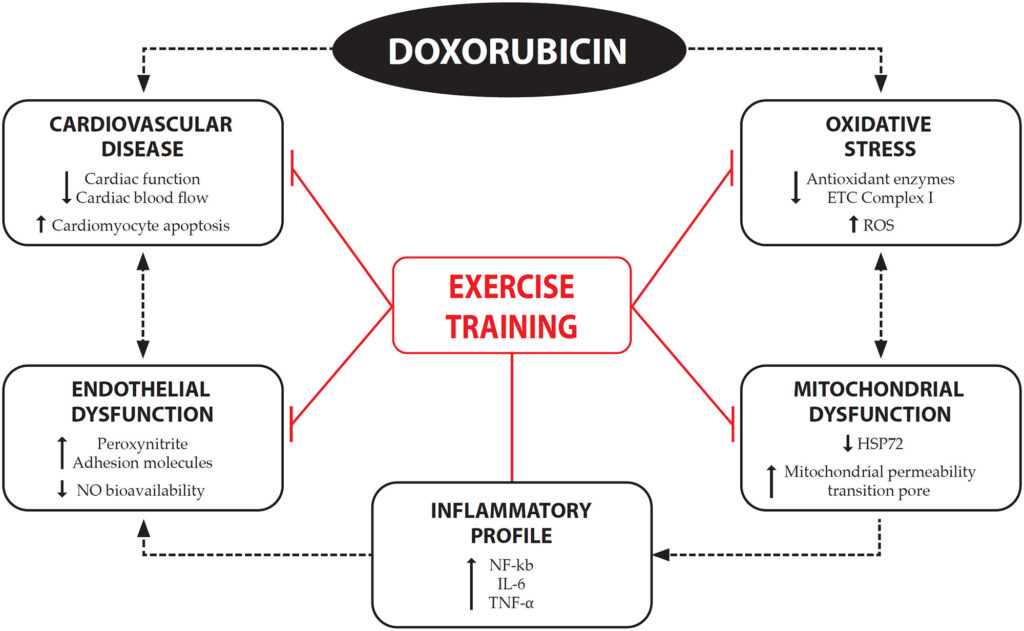
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a cytotoxic antineoplastic agent of the anthracycline family. It has been used as the first-line chemotherapy drug for treating various types of cancer, such as breast, lung and bladder cancer, and lymphoblastic leukemia. As any anthracycline, DOX is an effective chemotherapeutic drug. However, it holds a potentially lethal dose-dependent cardiovascular toxicity, which can manifest immediately or many years after chemotherapy, limiting its clinical application.
After the discontinuation of DOX treatment, a seven-year follow-up of 1,807 patients reported 33% death from heart diseases. Similarly, a 7.5% incidence of some cardiomyopathies was reported in pediatric sarcoma patients within an average of 34 months post-DOX treatment.
[…]
Palavras-chave: Doxorubicin; Cardiotoxicity; Exercise
1.275