International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 31/mar/2025;38:e20240136.
Assessment of Overweight/Obesity and Elevation of Blood Pressure in Schools in Rural and Urban Area in the Backlands of Bahia
Abstract
Background:
Childhood and adolescent obesity has been increasing, particularly in countries with greater social vulnerability. Given this context, assessing schoolchildren from Bahia’s backlands — a region known for its low-income population — is essential.
Objective:
To assess the frequency of overweight and obesity and their association with high blood pressure (BP) in children from urban and rural areas in four municipalities in the backlands of Bahia.
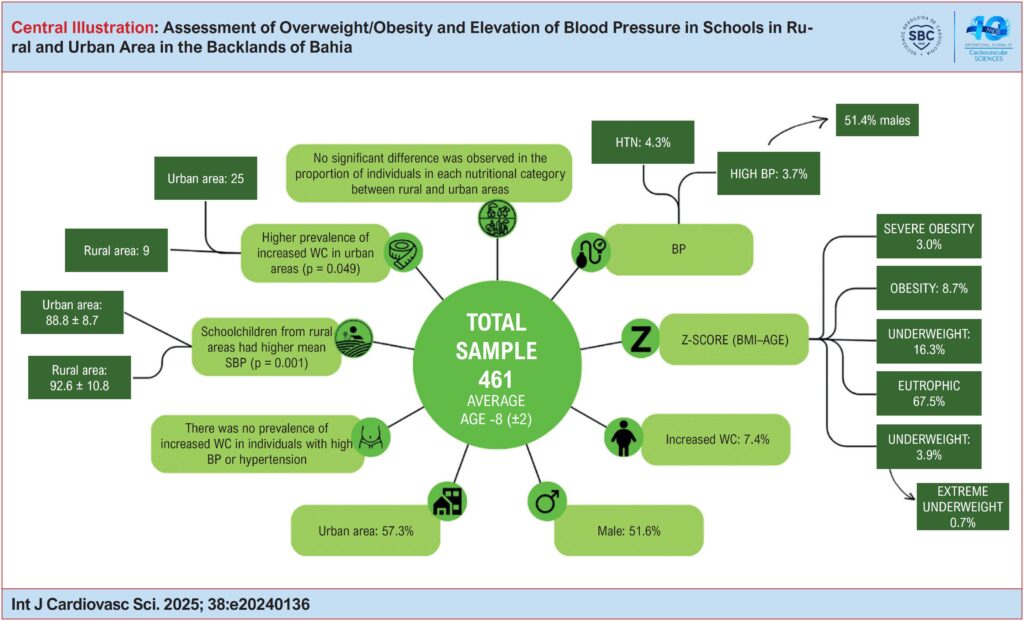
Methods:
This study is part of a project evaluating the impact of a school meal intervention on the health of children and adolescents in Bahia’s backlands. A subset of children aged five to ten from public schools in both rural and urban areas of four cities in Bahia’s backlands was selected through random and proportional sampling. The participants had their weight, height, waist circumference and BP measured using standardized protocols. The Body Mass Index (BMI) was expressed as a z-score to determine nutritional status. The Student’s t-test and Chi-square tests were used, with 5% statistical significance.
Results:
The sample consisted of 461 students, 264 (57.3%) from urban areas and 238 (51.6%) males. The prevalence of overweight was 27.9%, and that of increased waist circumference was 7.4%. High BP or hypertension had a prevalence of 8%. A significant difference (p = 0.049) was observed between rural and urban areas in relation to the increased waist circumference.
Conclusion:
The research revealed a high frequency of overweight, increased waist circumference and systemic BP in students, mainly those from urban areas.
Palavras-chave: Child; Hypertension; Obesity
294