International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 19/fev/2025;38:e20230189.
Inspiratory and Peripheral Muscle Training in Patients with Heart Failure: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background
Current guidelines recommend incorporating exercise and physical activity, such as inspiratory muscle training (IMT) and neuromuscular training, as adjunctive therapies alongside pharmacological treatments for patients with heart failure (HF).
Objective
To evaluate the effects of IMT and peripheral muscle training (PMT) on respiratory and peripheral muscle strength, lung function, and functional capacity in patients with HF.
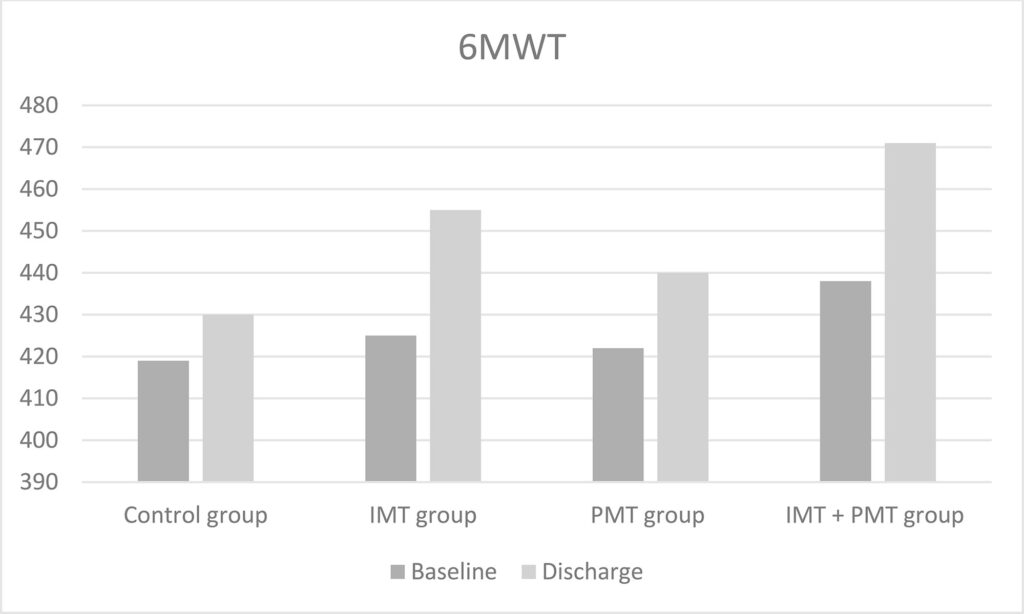
Methods
This is a randomized controlled trial. Prior to randomization, all patients were assessed with the 6-minute walk test, inspiratory muscle strength (maximum inspiratory pressure [MIP]), expiratory muscle strength (maximum expiratory pressure [MEP]), vital capacity (VC), peak expiratory flow (PEF), and peripheral muscle strength (using the Medical Research Council [MRC] scale). Participants were then randomly assigned to one of four groups: group 1 (control), group 2 (IMT), group 3 (PMT), or group 4 (IMT + PMT). This study was registered in the Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials (ReBEC) under number 2.382.698. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test was used to evaluate the four groups. The paired Student’s t test was used to compare the groups at different times. A p value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
A total of 52 patients were assessed. Regarding muscle strength, the group that underwent IMT combined with PMT showed a significant increase in both MIP (74 ± 15 at baseline versus 91 ± 16 at hospital discharge, p < 0.01) and MEP (92 ± 19 at baseline versus 102 ± 18 at hospital discharge, p < 0.01).
Conclusion
Based on these findings, it can be concluded that IMT combined with PMT has a positive impact in patients with HF, including improvements in both peripheral and respiratory muscle strength, reduction in dyspnea and fatigue, and enhanced tolerance to physical exercise.
Palavras-chave: Heart Failure; Breathing Exercises; Muscle Strength
503