International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 17/jan/2025;38:e20240099.
Mexiletine in The Treatment of Long QT Syndrome Type 2 in Infants: A Case Report
Introduction
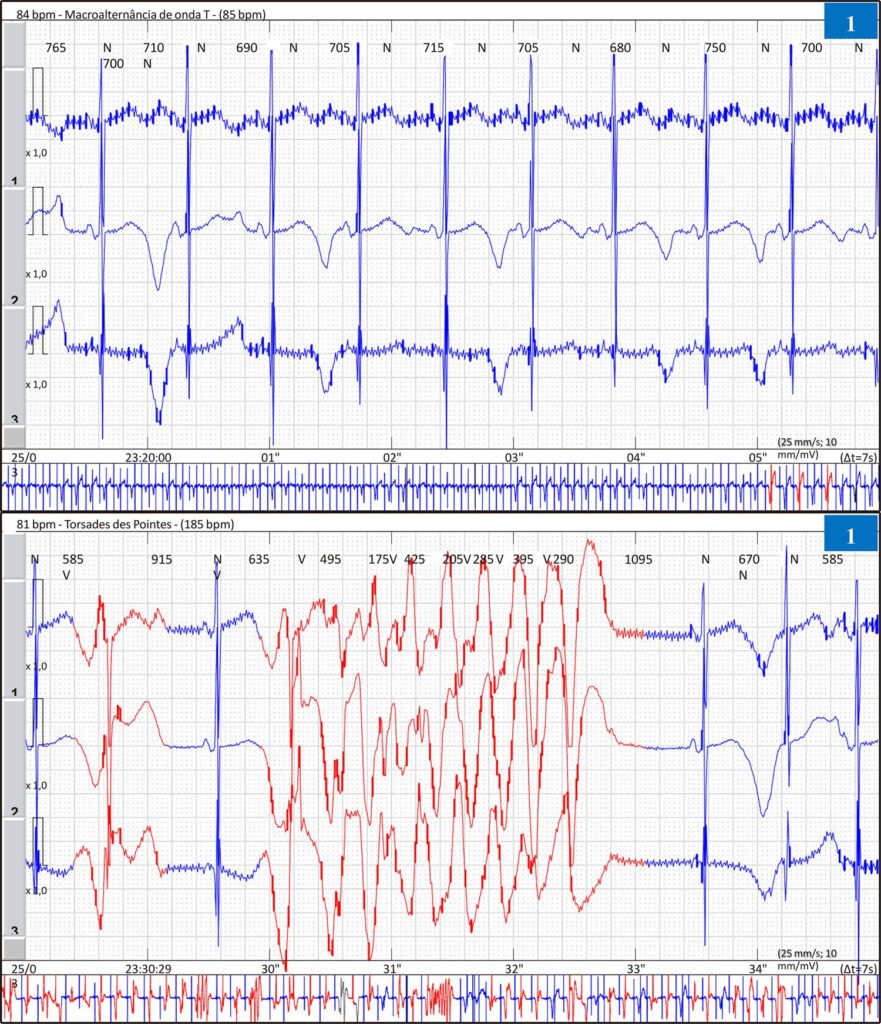
Congenital Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is one of the main causes of sudden cardiac death (SCD) in the pediatric age group, with a prevalence of approximately one case for every 2,000 newborns. The most prevalent inheritance is dominant, with the typical phenotype associated with cardiac manifestations.
The genetic alteration of LQTS is multigenic, with 17 main genes, and in 80% of the cases, it identifies: KCNQ1 (LQTL1), KCNH2 (LQTL2), and SCN5A (LQTL3). The LQTS type 2 (LQTS2) subtype alters the expression of potassium channels in myocytes, causing electrical instability and ventricular arrhythmias. The most common arrhythmia is Torsades de Pointes (TdP), a type of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, which can lead to syncope, seizures, and sudden death.
[…]
Palavras-chave: Long QT Syndrome; Cardiac Arrhythmias; Torsades de Pointes
513