International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 12/ago/2024;37:e20230085.
Development and Implementation of a Computerized Decision Support System for Screening Hypertension and Diabetes in a Resource-Constrained Region
Abstract
Background
Strategies aimed at improving the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are of utmost importance. Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) are guided by updated guidelines and may be capable of benefiting screening and early diagnosis initiatives in remote regions.
Objective
To develop a CDSS for screening hypertension and diabetes mellitus (DM), as well as to assess its feasibility and usability in the context of a primary care setting in a resource-constrained region.
Methods
This research focused on the strategy of screening hypertension and DM based on CDSS. A software was developed and implemented in 10 municipalities in the Northeast of the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, from April 2017 to October 2018. Patients of 30 to 69 years of age were attended by primary care practitioners using the software. A Likert-scale questionnaire with 15 questions to assess usability (System Usability Scale) and satisfaction was applied to the professionals at the end of study. Groups were compared by applying the chi-squared test for categorical variables. Statistical significance was considered as p < 0.05.
Results
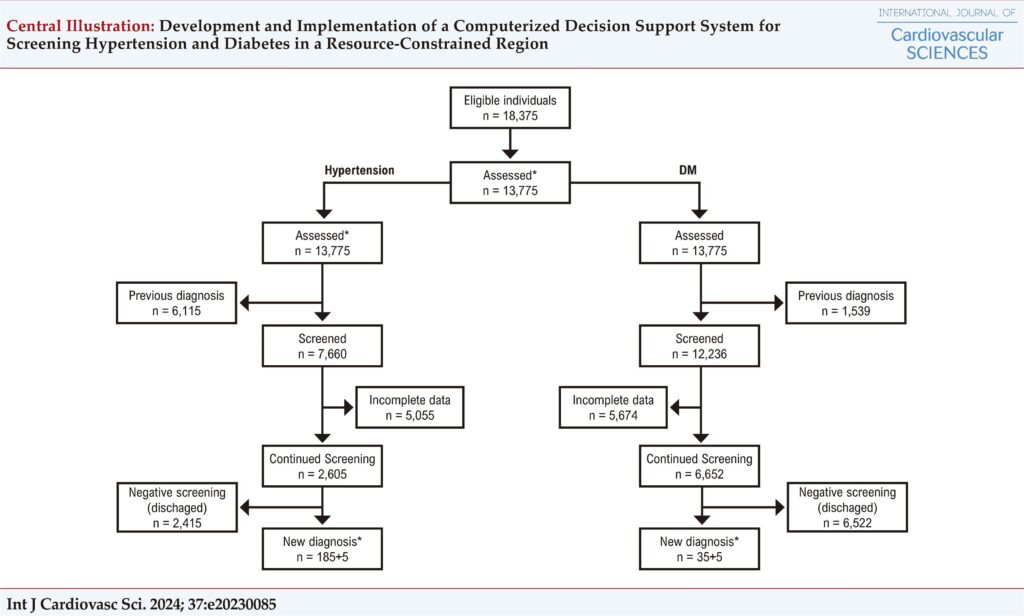
In the field study, 13,775 individuals were assessed; 185 patients were diagnosed with hypertension; 35 were diagnosed with DM, and 5 were diagnosed with both diseases. For the usability and satisfaction assessment, 258 healthcare professionals participated. Fifty-one percent considered their prior knowledge for the use of technologies to be good; 53.7% reported a desire to use the application frequently, and 78.4% would recommend the platform.
Conclusion
The implementation of a CDSS developed to assist in the screening of hypertension and DM was feasible in the context of a primary care setting in a resource-constrained region, with good user satisfaction.
Palavras-chave: Hypertension; Diabetes Mellitus; Telemedicine; Mass Screening; Clinical Decision Support Systems
687