International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 25/out/2021;34(5 Supl 1):22-3.
Cardiotrophin-1 in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: Does it Have a Role?
Acute coronary syndromes are among the most common diagnoses in the emergency department (ED). It has been estimated that 300,000 to 400,000 cases are seen each year in Brazil. The diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is made on the basis of symptoms, electrocardiogram, and biological markers of myocardial necrosis. Troponins are the most specific cardiac markers, and in the era of highly sensitive assays, they have been shown to make the exclusion of AMI in the ED more rapid, being particularly helpful in patients with atypical presentations.
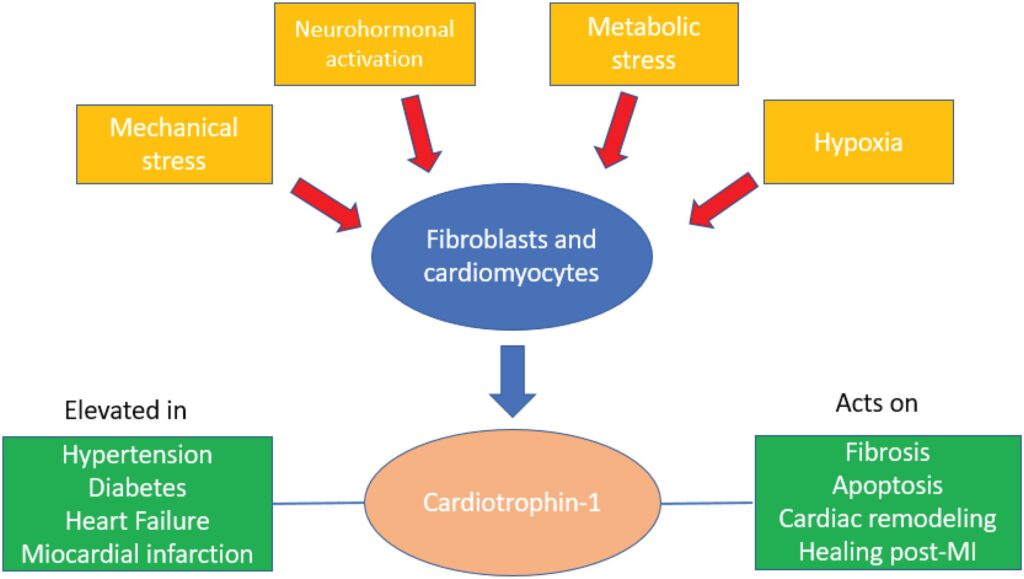
Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) is a member of the interleukin-6 superfamily of proinflammatory cytokines. It is expressed in many tissues, including heart and vessels. CT-1 is upregulated in cardiac fibroblasts and cardiomyocytes in response to mechanical, humoral, metabolic, and hypoxic stress (). It is elevated in the myocardium and plasma of heart failure (HF) patients and has also been associated with hypertension, diabetes, cardiac hypertrophy, and fibrosis, both in patients and experimental studies., CT-1 is expressed after an AMI and seems to be involved in the healing and remodeling process that occurs after myocardial infarction., In the study by Freed et al., CT-1 was able to initiate each of the processes related to scar formation, including fibroblast migration and proliferation, and collagen synthesis.
[…]
Palavras-chave: Coronary Artery Disease; Myocardial Infarction; Electrocardiography/methods; Biomarkers; Cytokines
1.352