International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 18/Nov/2024;37:e20240109.
The Association Between IL-4 Expression and Thrombus Events in Rheumatic Heart Disease Patients
Abstract
Background:
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is the leading cause of valve disease in developing countries, with intracardiac thrombus events as one of the frequent manifestations. Based on Trias Virchow, a thrombus occurs because of endothelial injury, blood flow abnormality, and hypercoagulability. In RHD, this condition is caused by inflammation, mitral stenosis (MS), and atrial fibrillation (AF). Pro-inflammatory cytokines promote thrombus formation, and anti-inflammatory cytokines inhibit it. IL-4 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that can potentially inhibit thrombus formation because it can inhibit other pro-inflammatory cytokines and polarize M2 macrophages.
Objectives:
This study aims to know the association of IL-4 expression with thrombus events in RHD patients.
Methods:
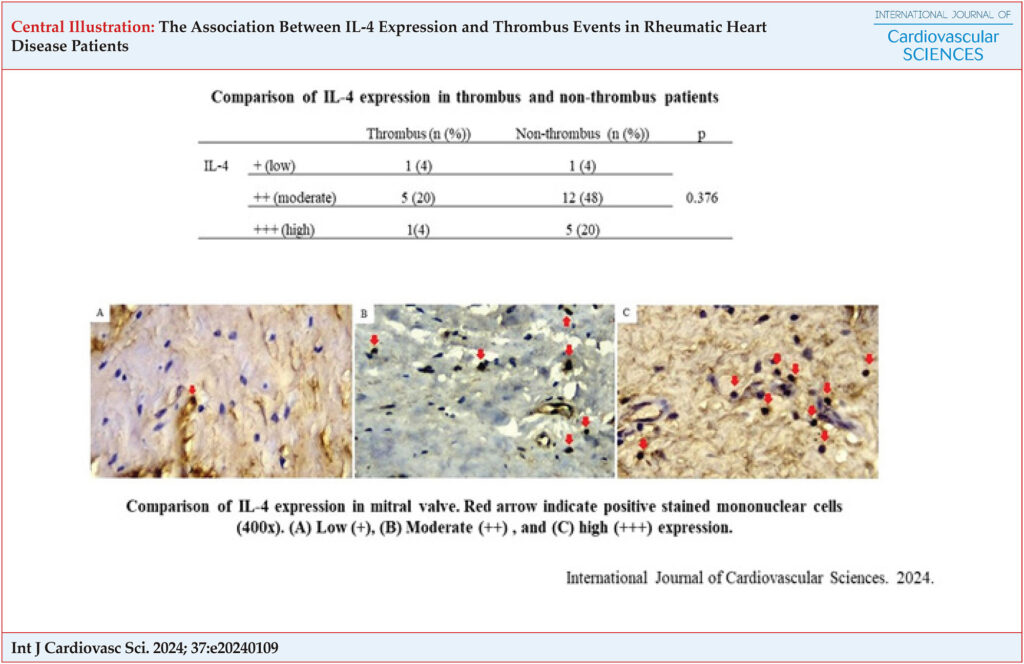
Twenty-five (25) patients enrolled in this study were diagnosed with RHD and underwent mitral valve replacement surgery. Valve tissues were collected for histopathological and immunohistochemical examination using IL-4. Thrombus event obtained from echocardiography result. The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare IL-4 expression in thrombus and non-thrombus patients. A p-value of less than 0.05 (p<0.05) was considered the significance level.
Results:
Of the 25 patients, 88% were older than 30 years. Thrombus occurs in 28% of RHD patients and is associated with AF (p 0.001). Patients with moderate and high IL-4 expression did not have less thrombus than patients with low IL-4 expression.
Conclusions:
Intracardiac thrombus formation in RHD patients is not associated with IL-4 expression but is strongly associated with AF. Further research that identifies other cytokines coexisting with IL-4 at the site of injury may reveal better insight into the event.
512