International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 01/Apr/2018;31(2):143-51.
Study with a Portable Gas Analyzer of the 6-Minute Walk Test in Heart Failure with Normal Ejection Fraction
DOI: 10.5935/2359-4802.20180001
Abstract
Background:
Few studies have used portable gas analyzers during the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) in patients with heart failure and normal ejection fraction (HFNEF).
Objectives:
To analyze the kinetics of hemodynamic, ventilatory, and metabolic variables in patients with HFNEF during the T6m using a portable gas analyzer.
Methods:
Prospective, analytical study with an intentional, non-probabilistic, convenience sample. In total, 24 patients with HFNEF and past hospital admissions due to a clinical diagnosis of heart failure (HF) were included using the 2007 criteria established by the European Society of Cardiology. Three assessments were performed: 6MWT familiarization, 6MWT with the portable gas analyzer, and cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET).
Results:
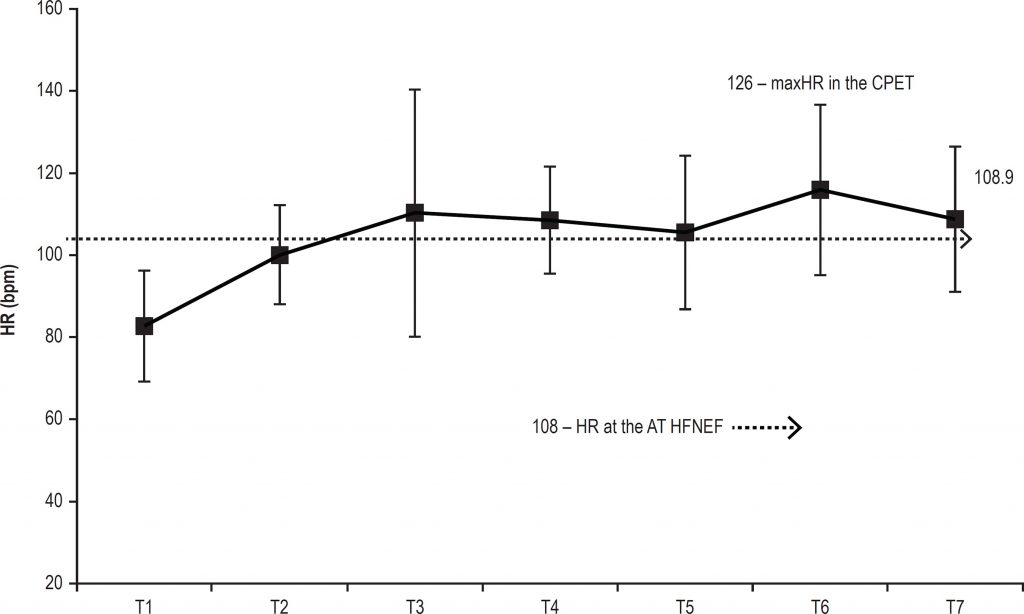
The heart rates (HRs) and the peak VO2 at the end of the 6MWT corresponded to 85.7% and 86.45% of the values obtained during the CPET. The final HRs after the T6m were equivalent to those obtained at the CPET anaerobic threshold (AT), with relative VO2 values at the end of the 6MWT above the VO2 of the CPET AT. There was no difference between the maximum respiratory quotient (RQ) values in these two tests, which were both above 1.0. The VE/VO2 slope descended initially and then ascended significantly after the fifth minute of the test, estimating the identification of the AT.
Keywords: Heart Failure; Blood Gas Analysis; Stroke Volume; Exercise; Walk Test
633