International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 26/May/2021;34(5 Supl 1):139-45.
Renal Sympathetic Denervation Using a Novel Device: A Clinical Case Discussion and Literature Update
Introduction
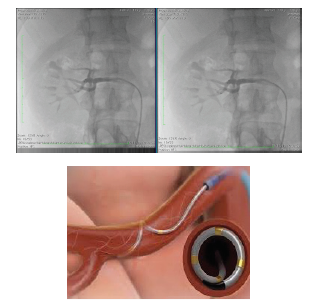
Resistant hypertension (RH) is directly related to increased mortality, severe renal changes, and cardiac and cerebrovascular diseases, due to lack of adequate drug treatment. Cardiovascular disease mortality increases progressively and linearly as BP increases, whereas BP lowering is associated with significantly reduced risks. – Increased sympathetic tone in renal arteries is one of the major components of RH, and catheters have been developed using several technologies which allow for radiofrequency ablation (RA) and blood pressure (BP) reduction. The discussions and controversies about the effectiveness of this treatment are quite broad, especially when associated with the use of new devices. In this clinical case study, with an 18-month follow-up, we describe the development of knowledge regarding this technique and its evidence basis.
[…]
476