International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 06/Aug/2025;38:e20240241.
Comparison Between Two Prevention and Control Programs for Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in an Oil Company
Abstract
Background:
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death in the world, and companies can implement prevention and control actions aimed at reducing risk factors among their workers.
Objectives:
To verify whether the result of model A of a CVD prevention and control program was superior to model B in reducing the cardiovascular risk (CVR) of individuals from an oil company.
Methods:
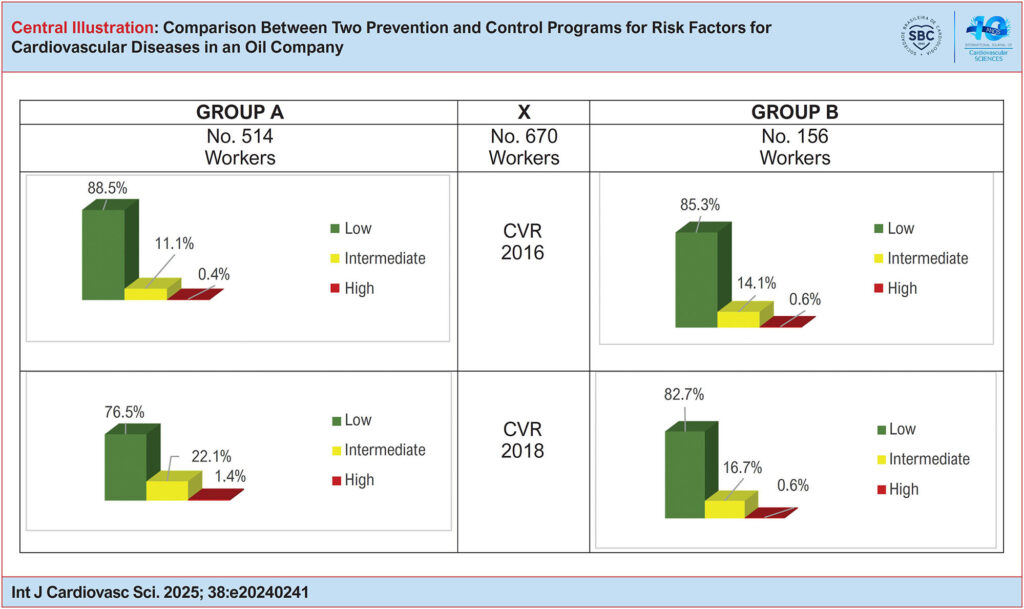
Retrospective evaluation of secondary data from a restricted and fixed cohort of 670 workers, from 01/01/2016 to 12/31/2018. The workers were divided by program model into Group A (514) and Group B (156). The 2016 CVR was compared with that of 2018, within and between groups, as well as the mean and prevalence of risk factors for CVD. Statistical analysis was set at a significance level of 5%.
Results:
Group A improved the level of physical activity (PAL), consumption of fruits and vegetables, and consumption of alcohol, but the “high” CVR increased from 0.4% in 2016 to 1.4% in 2018 (p<0.01). In Group B there was no change in the workers’ health profile, but the percentage of individuals with "intermediate" CVR increased from 14.1% to 16.7% (p=0.01).
Conclusions:
The actions developed by the company had a positive impact on the way of life of workers covered by the model A program; however, they were not sufficient to reduce CVR in this group.
164